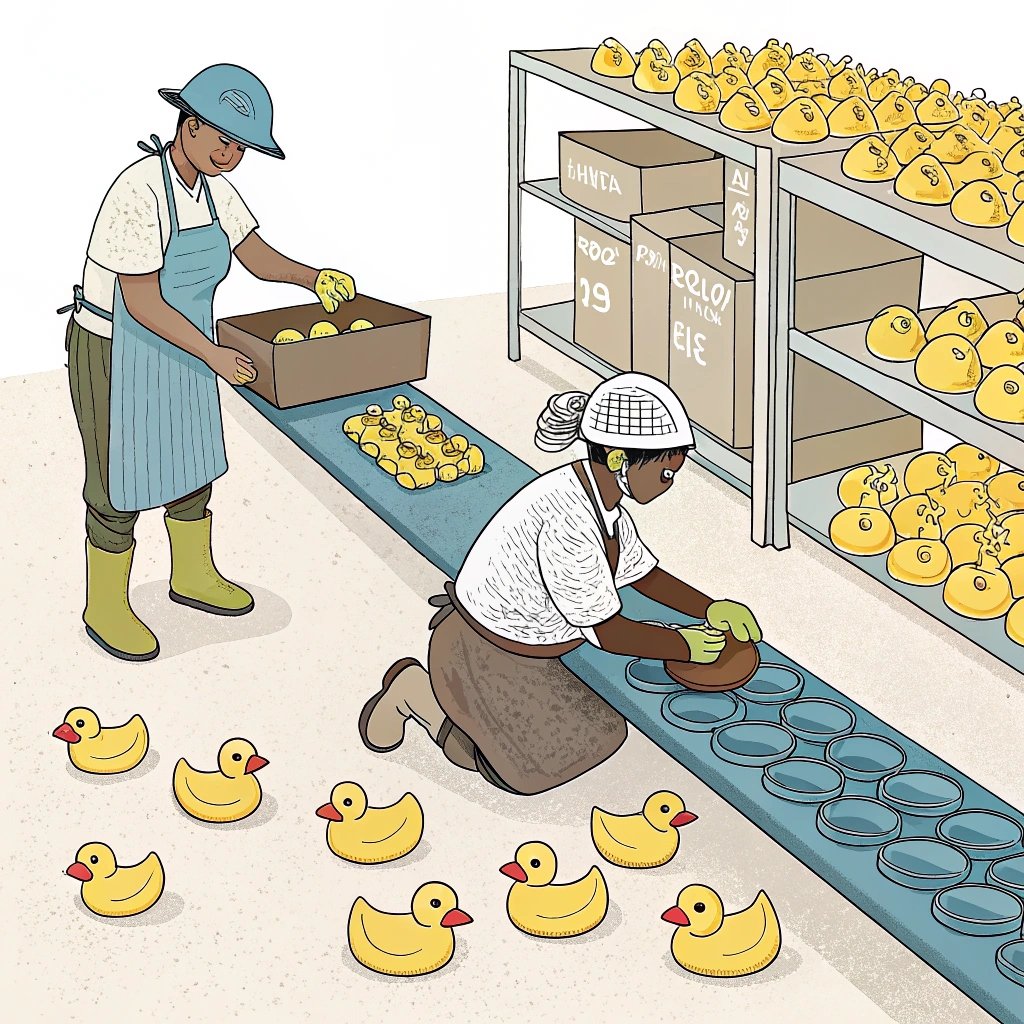
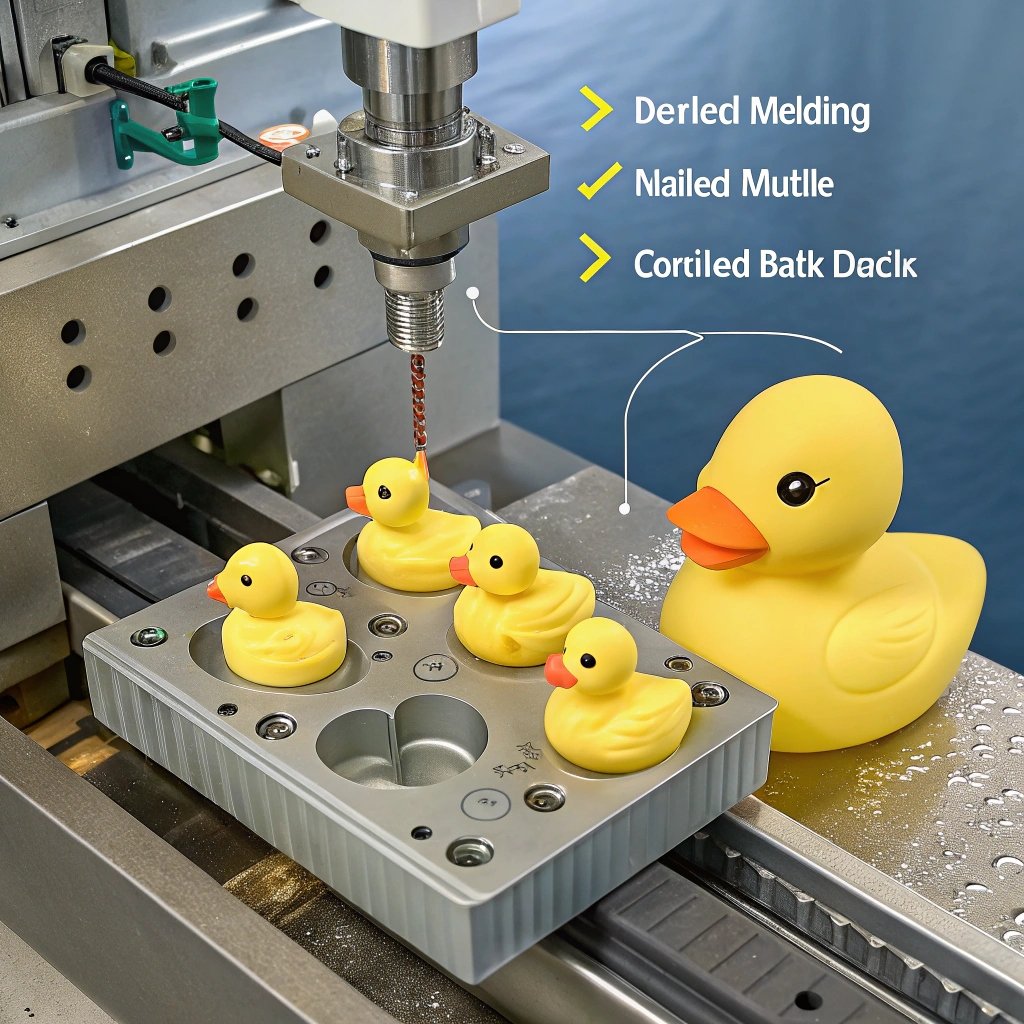
Rubber ducks are more than just bath-time toys—they’re the result of a precise and fascinating manufacturing process.
Rubber ducks are typically manufactured using injection molding[^1], a process where molten rubber is injected into molds to form the desired shape.
What Is the Manufacturing Process of Rubber Molding?
Rubber molding for ducks primarily uses injection molding[^2], where heated rubber is injected into molds to form the duck shape.
Key Steps in Rubber Molding:
- Material Preparation: Raw rubber is mixed with additives to enhance flexibility and durability.
- Injection Molding: Rubber is heated and injected into pre-designed molds.
- Cooling and Ejection: The molded duck is cooled and removed from the mold.
- Finishing: Excess material is trimmed, and paint or details are applied.
What Is the Rubber Ducky Method?
The rubber ducky method involves explaining code line-by-line to an inanimate object[^3] to identify bugs.
How It Works:
- Explain Your Code: Walk through each line aloud.
- Identify Issues: Talking through logic exposes mistakes.
- Clarify Thinking: Forces clear articulation of problems.
What Is the Manufacturing Process of Rubber Hose?
Rubber hoses are commonly produced through extrusion[^4], where rubber is shaped into a continuous profile.
Manufacturing Steps:
- Compounding: Mixing raw rubber with fillers and stabilizers.
- Extrusion: Rubber is forced through a die to create shape.
- Curing: The extruded rubber is vulcanized for durability.
- Finishing: Cutting, inspecting, and adding fittings.
What Is Rubber Duck Engineering?
"Rubber duck" engineering refers to wheeled excavators nicknamed for their rubber tires and duck-like shape[^5].
Characteristics:
- Mobility: Rubber tires allow travel on roads.
- Versatility: Operates in urban and rural sites.
- Efficiency: Quick to reposition without transport trucks.
How Long Do Rubber Ducks Last?
Typically, rubber ducks can last several years[^6], but exposure to sunlight and harsh conditions may degrade them faster.
Factors Affecting Longevity:
- Material Quality: Better rubber resists cracking.
- Environmental Exposure: UV light accelerates breakdown.
- Usage: Frequent squeezing or bending wears material.
What Is the Process of Manufacturing Rubber?
The process includes harvesting latex, compounding, shaping, and vulcanization[^7] to produce durable rubber items.
Manufacturing Stages:
- Latex Collection: Extracting sap from rubber trees.
- Compounding: Adding pigments, sulfur, and fillers.
- Shaping: Using molds or extrusion.
- Vulcanization: Heating with sulfur to strengthen.
What Are the Four Methods of Processing Rubber?
The four primary methods are extrusion, molding, calendaring, and coating[^8].
Processing Methods:
- Extrusion: Continuous shapes like hoses.
- Molding: 3D items like toys or seals.
- Calendaring: Rolling into thin sheets.
- Coating: Covering fabrics or surfaces with rubber.
What Is Molding Manufacturing Process?
Molding involves shaping materials by introducing them into a mold[^9] where they solidify into the desired form.
Types of Molding:
- Injection Molding: Molten material forced into molds.
- Compression Molding: Material pressed into shape.
- Transfer Molding: Hybrid of injection and compression.
What Is the Method of Fabrication of Rubber?
Common fabrication methods include molding, extrusion, and calendaring[^10], each suited to different product types.
Fabrication Techniques:
- Molding: For complex shapes.
- Extrusion: For tubing and profiles.
- Calendaring: For sheets and coatings.
What Chemical Process Is Used to Make Rubber?
Vulcanization is the key chemical process[^11], involving sulfur and heat to strengthen rubber.
Vulcanization Details:
- Cross-Linking: Sulfur bonds increase strength.
- Improved Properties: Boosts elasticity and durability.
- Applications: Tires, seals, toys.
What Is the Raw Material for Rubber Molding?
Raw materials include natural rubber and synthetic rubbers like EPDM, SBR, and NBR[^12].
Material Types:
- Natural Rubber: Harvested from rubber trees.
- Synthetic Rubber: Engineered for specific traits.
Conclusion
Rubber ducks combine playful design with industrial precision, blending material science, molding techniques, and creative finishing to create a timeless toy.
[^1]: Discover how injection molding shapes rubber ducks. Query: How are rubber ducks manufactured?
[^2]: Understand rubber molding for toy production. Query: What is the rubber molding process?
[^3]: Learn about the rubber ducky method in debugging. Query: What is rubber ducky debugging?
[^4]: See how rubber hoses are made via extrusion. Query: How is a rubber hose manufactured?
[^5]: Find out why excavators are called rubber ducks. Query: What is rubber duck engineering?
[^6]: Know how long rubber ducks last. Query: How long do rubber ducks last?
[^7]: Explore the rubber manufacturing process. Query: What are the steps to make rubber?
[^8]: Learn the four rubber processing methods. Query: What are rubber processing methods?
[^9]: Understand molding in manufacturing. Query: What is molding process?
[^10]: Find rubber fabrication techniques. Query: What are rubber fabrication methods?
[^11]: Explore vulcanization in rubber production. Query: What is vulcanization?
[^12]: Know raw materials used for rubber molding. Query: What raw material is used in rubber molding?